Write a Program That Reads the Contents of the Two Files Into Two Separate Lists
This tutorial covers the post-obit topic – Python Write File/Read File. It describes the syntax of the writing to a file in Python. Likewise, information technology explains how to write to a text file and provides several examples for help.
For writing to a file in Python, you would need a couple of functions such equally Open() , Write() , and Read() . All these are built-in Python functions and don't crave a module to import.
There are majorly two types of files you lot may have to collaborate with while programming. One is the text file that contains streams of ASCII or UNICODE (UTF-eight) characters. Each line ends with a newline ("\n") char, a.grand.a. EOL (End of Line).
Another type of file is called binary that contains machine-readable data. It doesn't have, so-called line as there is no line-ending. Only the awarding using information technology would know nigh its content.
Anyways, this tutorial will strictly tell yous to piece of work with the text files only.
Python Write File Explained with Examples
Permit'due south brainstorm this tutorial by taking on the first call required to write to a file in Python, i.eastward., Open() .
Open File in Python
You lot get-go accept to open up a file in Python for writing. Python provides the born open() part.
The open() function would return a handle to the file if it opened successfully. It takes two arguments, equally shown beneath:
''' Python open up file syntax ''' file_handle = open("file_name", "access_mode") The first argument is the proper noun or path of the file (including file name). For example – sample_log.txt or /Users/john/home/sample_log.txt.
And the 2nd parameter (optional) represents a way to open the file. The value of the "access_mode" defines the operation you want to perform on it. The default value is the READ just style.
# Open a file named "sample_log.txt" # It rests in the same directory as you are working in. file_handle1 = open("sample_log.txt") # Let's open up the file from a given path file_handle2 = open("/Users/john/home/sample_log.txt") File Open Modes
Information technology is optional to pass the mode argument. If y'all don't set information technology, then Python uses "r" as the default value for the access way. It means that Python will open a file for read-only purpose.
Notwithstanding, there are a full of half-dozen access modes bachelor in python.
- "r" – It opens a text file for reading. It keeps the offset at the get-go of the file. If the file is missing, then it raises an I/O mistake. It is also the default mode.
- "r+" – It opens the file for both READ and WRITE operations. Information technology sets the first at the start of the file. An I/O error occurs for a non-existent file.
- "w" – It opens a file for writing and overwrites whatsoever existing content. The handle remains at the starting time of the data. If the file doesn't exist, then it creates ane.
- "w+" – It opens the file for both READ and WRITE operations. Residue, it works the aforementioned every bit the "due west" way.
- "a" – It opens a file for writing or creates a new one if the file not found. The handle moves to the end (EOF). Information technology preserves the existing content and inserts data to the stop.
- "a+" – It opens the file for both READ and WRITE operations. Rest, information technology works the same as the "a" mode.
Check out a few examples:
# Open a file named "sample_log.txt" in write manner ### # Information technology rests in the same directory every bit you are working in. file_handle1 = open("sample_log.txt", "w") # Open up the file from a given path in append mode file_handle2 = open("/Users/john/abode/sample_log.txt", "a") Write File in Python
Python provides two functions to write into a text file: Write() and Writelines() .
1. write() – Let's first apply write() for writing to a file in Python. This function puts the given text in a single line.
''' Python write() function ''' file_handle.write("some text") But, first, open any IDE and create a file named "sample_log.txt" for our test. Don't make whatever other changes to it.
Delight notation – If you try to open a file for reading and it doesn't exist, then Python will throw the FileNotFoundError exception.
To edit this file from your Python program, nosotros've given the following code:
# A unproblematic example - Python write file ### file_handle = open up("sample_log.txt","w") file_handle.write("Hello Everyone!") file_handle.write("It is my offset effort to write to a file in Python.") file_handle.write("I'll first open the file and and so write.") file_handle.write("Finally, I'll close it.") file_handle.close() We've opened the file in "westward" way, which means to overwrite anything written previously. So, after you open it and see its content, yous'll find the new text in four different lines.
2. writelines() – The writelines() function takes a list of strings as the input and inserts each of them equally a carve up line in one go. You can bank check its syntax below:
''' Python writelines() function ''' file_handle.writelines([str1, str2, str3, ...])
Append File in Python
Yous also need to know how to append the new text to an existing file. In that location are two modes available for this purpose: a and a+.
Whenever you open a file using one of these modes, the file offset is set to the EOF. And then, you can write the new content or text adjacent to the existing content.
Let's empathise information technology with a few lines of lawmaking:
We'll first open a file in "a" style. If you run this case the offset time, then it creates the file.
# Python Suspend File in "a" manner Case ### fh = open("test_append_a.txt", "a") fh.write("Insert Get-go Line\n") fh.write("Append Side by side Line\n") And so far, two lines take been added to the file. The second write functioning indicates a successful suspend.
Now, you'll see the difference between the "a" and "a+" modes. Let'due south try a read functioning and see what happens.
fh.read() # io.UnsupportedOperation: not readable
The above line of code would fail equally the "a" mode doesn't allow READ. And then, close it, open, and so practice a read operation.
fh.close() # Close the file fh = open("test_append_a.txt") # Open up in the default read mode impress(fh.read()) # Now, read and print the unabridged file fh.close() The output is something similar:
Insert Start Line Append Side by side Line
Let'due south now try appending using the "a+" fashion. Check out the below code:
# Python Suspend File in "a+" mode Example ### fh = open("test_append_aplus.txt", "a+") fh.write("Insert First Line\n") fh.write("Suspend Next Line\n") fh.seek(0) # Prepare offset position to the start print(fh.read()) # READ is sucess in a+ mode ## Output # Insert First Line # Append Adjacent Line fh.write("Append Another Line\n") # WRITE another line to the text file fh.seek(0) # Set the beginning for reading print(fh.read()) # Do the READ operation once more ## Output # Insert Starting time Line # Append Next Line # Append Another Line Read File in Python
For reading a text file, Python bundles the following iii functions: read() , readline() , and readlines()
one. read() – Information technology reads the given no. of bytes (N) equally a string. If no value is given, so information technology reads the file till the EOF.
''' Python read() function ''' #Syntax file_handle.read([North])
2. readline() – Information technology reads the specified no. of bytes (N) as a string from a single line in the file. Information technology restricts to one line per call fifty-fifty if N is more than than the bytes available in one line.
''' Python readline() part ''' #Syntax file_handle.readline([N])
3. readlines() – Information technology reads every line presents in the text file and returns them equally a list of strings.
''' Python readlines() function ''' #Syntax file_handle.readlines()
It is then easy to use the Python read file functions that y'all can check yourself. Just type the following code in your IDE or the default Python IDE, i.due east., IDLE.
# Python Read File Example ### fh = open("sample_log.txt") # No demand to specify the mode as READ is the default way print(fh.read()) # Expect the whole file to get printed here fh.seek(0) # Reset the file showtime to the beginning of the file print(fh.readline()) # Print just the beginning line from the file fh.seek(0) # Reset the offset again print(fh.readlines()) # Print the list of lines fh.shut() # Close the file handle Please note that the Python seek() function is needed to modify the position of file beginning. It decides the betoken to read or write in the file. Whenever you do a read/write operation, information technology moves along.
Shut File in Python
File handling in Python starts with opening a file and ends with closing information technology. Information technology means that you must close a file after yous are finished doing the file operations.
Closing a file is a cleanup activeness, which ways to free up the system resources. It is also essential because you can only open up a express number of file handles.
Also, delight note that whatever attempt to access the file afterwards closing would throw an I/O error. You may have already seen u.s. using it in our previous examples in this post.
With Statement in Python
If y'all want a cleaner and elegant way to write to a file in Python, then try using the WITH statement. It does the automatic clean up of the system resource like file handles.
Also, it provides out of the box exception handling (Python try-except) while you lot are working with the files. Check out the following example to see how with statement works.
# Write File in Python using WITH statement ## # Sample code(ane) Write to a text file fh = open("sample_log.txt", "westward") endeavor: fh.write("I love Python Programming!") finally: fh.close() # Sample lawmaking(2) Write using with statement with open up("sample_log.txt", "w") equally fh: fh.write("I dearest Python even more than!!") Working sample lawmaking
Below is a full-fledged case that demonstrates the usage of the following functions:
- Python Write file using write() & writelines()
- Python Read file operations using read(), readline(), and readlines()
# Python Write File/ Read File Example ### print("### Python Write File/ Read File Instance ###\n") file_handle = open("sample_log.txt", "w") list_of_strings = ["Python programming \n","Web development \n","Agile Scrum \n"] # Write a newline char at each line in the file file_handle.write("Welcome! \n") file_handle.writelines(list_of_strings) file_handle.close() # Open the text file for reading file_handle = open("sample_log.txt", "r+") # Read the entire text file and display its content print("1) Demonstrate Python read() function") out = file_handle.read() impress("\n>>>Python read() file output:\n{}".format(out)) # At present, set the file offset to the get-go file_handle.seek(False) # Read the beginning line from the text file using readline() impress("2) Demonstrate Python readline() office") out = file_handle.readline() print("\n>>>Python readline() file output:\northward\tLine#ane{}".format(out)) # Once more, position the file start to zero file_handle.seek(Faux) # Read the entire text file using readlines() print("3) Demonstrate Python readlines() part") out = file_handle.readlines() file_handle.close() print("\n>>>Python readlines() file output:") for i, line in enumerate(out): print("\tLine#{} {}".format(i+ane, line)) This Python programme generates the post-obit output:
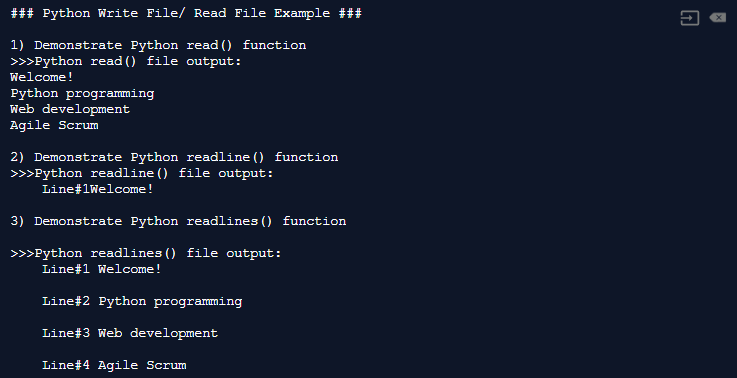
Try the Quiz
We've now come to the closure of this Read/Write File in Python tutorial. If y'all have read it from the starting time to end, and so file handling would be on your tips. However, nosotros recommend the following quizzes to attempt.
These are quick questionnaires to test how much knowledge have you retained after reading the above stuff.
- Python File Treatment Quiz – Part1
- Python File Treatment Quiz – Part2
Besides, yous must use these concepts in your projects or tin also write some hands-on code to solve real-time issues. It'll certainly assistance yous grasp faster and recollect ameliorate.
Past the style, if yous wish to acquire Python from scratch to depth, then practice read our step by step Python tutorial .
campbellinectelithe.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.techbeamers.com/read-write-file-in-python/
0 Response to "Write a Program That Reads the Contents of the Two Files Into Two Separate Lists"
Post a Comment